Manufacturing's New Frontier is Here. And The Time for 5G is Now!
Unlike previous wireless evolutions that focused primarily on enabling consumer mobile phone communications, 5G shifts focus significantly to empower the factory of the future. Specifically, 5g technology focuses on providing enhanced ultra-reliability, low latency and time sensitive network. "Those are the central features for industrial IoT applications," says Qualcomm Principal Engineer Dr. Xiaoxia Zhang during her Dec. 2 keynote at the IndustryWeek Manufacturing & Technology Virtual Conference.
And, as the pandemic has spotlighted, smart factories are no longer futuristic dreams. For manufacturers to thrive in the new frontier, it’s crucial to embrace the many technologies enabling further automation and accurate remote access to the shop floor. This is where 5G can make a meaningful difference.
Understanding the biggest benefits
Ultra-reliability and low latency. These are both crucial factors that make 5G attractive within industrial applications. Consider the use case of an industrial robot for motion control. 5G can meet latency demands as stringent as one millisecond with reliability can go up to 10 to the minus six. Or for manufacturers using head-mounted AR units, 5G can support the data rates can commonly go up to gigabits per second. With 5G, whenever one wireless signal is degraded by a moving object, the signals from the other GRPc can still reach the 5g device to ensure successful package delivery.
Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) capabilities. TSN is often key requirement for industry automation applications. With 5G TSN, manufactures can achieve time synchronization across all the devices. The latest release tackles the problem by treating 5G as a TSN bridge. When an incoming packet goes through the 5g Network, the 5G TSN adapter records incoming time. When the packet leaves the 5g network, it also records the outgoing time. Based on these times, approach and field is computed and passed to the device allowing for perfect time synchronization with each other.
Although currently on its 16th release, 5G is not at the end of the 3GPP strategy - nor are the potential benefits for manufacturers. For instance, the next standard release will introduce improved capability for high precision positioning where manufacturers will see accuracy to 20 centimeters.
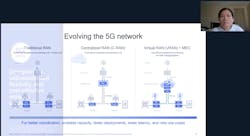
Should smart manufacturers consider a private network?
Of course, just because a factory has use cases that could benefit from 5G does not mean their plant locations are in geographical alignment with a public mobile provider's 5G deployment priorities. Fortunately, this is does not take the capabilities off the table for manufacturers aiming to benefit from 5G. As Dr. Zhang discusses, deploying a private network is a feasible, and in many instances more attractive, option for today’s smart manufacturers.
Improved Privacy. A 5g private network allows a dedicated local network with dedicated resources managed independently from the public network. It also offers greater privacy and security without going to the central cloud.
Optimized performance. A 5G private network all resources are dedicated to local applications. For example, if a factory owner needs ultra-reliability and low latency, a private network can emphasize or optimize those aspects.
Flexibility. As a global standard, 5G has a vast ecosystem and an extensive roadmap. This means by deploying a 5g private network, the opportunity and flexibility exist to continue integrating features that come out in future releases.
According to Dr. Zhang, the opportunity also exists for mobile operators to offer the private network as a service. Under this model mobile operators can leverage the licensing option as well as tap into their expertise as operators.
To see her full presentation, you can register here to gain access to all keynotes, workshops and tours for up to 90 days
About the Author
Peter Fretty
Technology Editor
As a highly experienced journalist, Peter Fretty regularly covers advances in manufacturing, information technology, and software. He has written thousands of feature articles, cover stories, and white papers for an assortment of trade journals, business publications, and consumer magazines.